
The term “dark web” conjures up images of a shadowy netherworld of cybercrime, espionage, drugs, and guns. In reality “dark web” sites are simply websites ending in .onion that need to be accessed through a special browser, The Onion Router (Tor).
Cybersecurity firms have long sold “dark web monitoring” packages, with each package meaning something slightly different.
In many cases, practitioners have struggled to find value in monitoring the dark web, particularly where a vendor sells them on a comprehensive package but doesn’t align the value with the organization's security needs.
In other cases organizations may believe they are too small for dark web monitoring to be valuable, but in many cases startups and other small organizations are targeted because they are small.
This article is going to examine the security value in dark web monitoring with a particular emphasis on deconfusion.
Dark Web Breach Monitoring
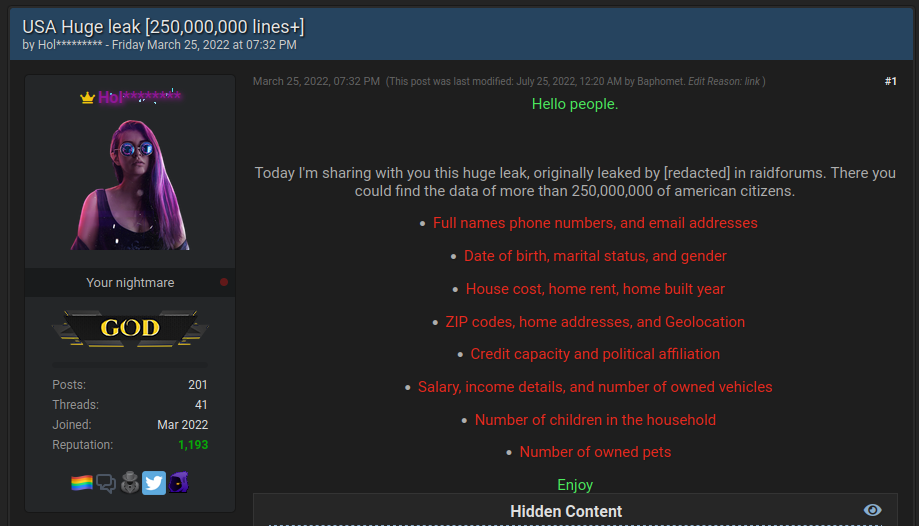
One of the first and most important distinctions to make is monitoring .onion sites, versus the files hosted on them. Have you ever received an alert that your credentials to a website or application were compromised? When threat actors breach a service (or find an exposed cloud bucket!) they often end up with huge databases of user credentials to that service.
Fresh sets of breached credentials are distributed on the aptly named Breach Forums and other .onion sites in large files.
Other threat actors are then able to purchase this data, and replay the breached credentials against other likely websites the users had signed up for. For example, if a threat actor knows you recently used an email address and password on a business accounting application, they can try those same credentials on business banking websites.
This form of monitoring is one of the most basic but also most actionable forms of dark web monitoring.
Source: Flare
Dark Web Forum, Marketplace, and Ransomware Monitoring
The next level up of monitoring is to collect and archive the actual content of dark web pages. This encompasses things like conversations about cybercrime, tactics, techniques, and procedures, and listings for corporate access that threat actors are selling.
The real use-case here is for sophisticated organizations that have not only a need to identify leaked credentials but want to proactively understand the cybercrime ecosystem and how it’s evolving.
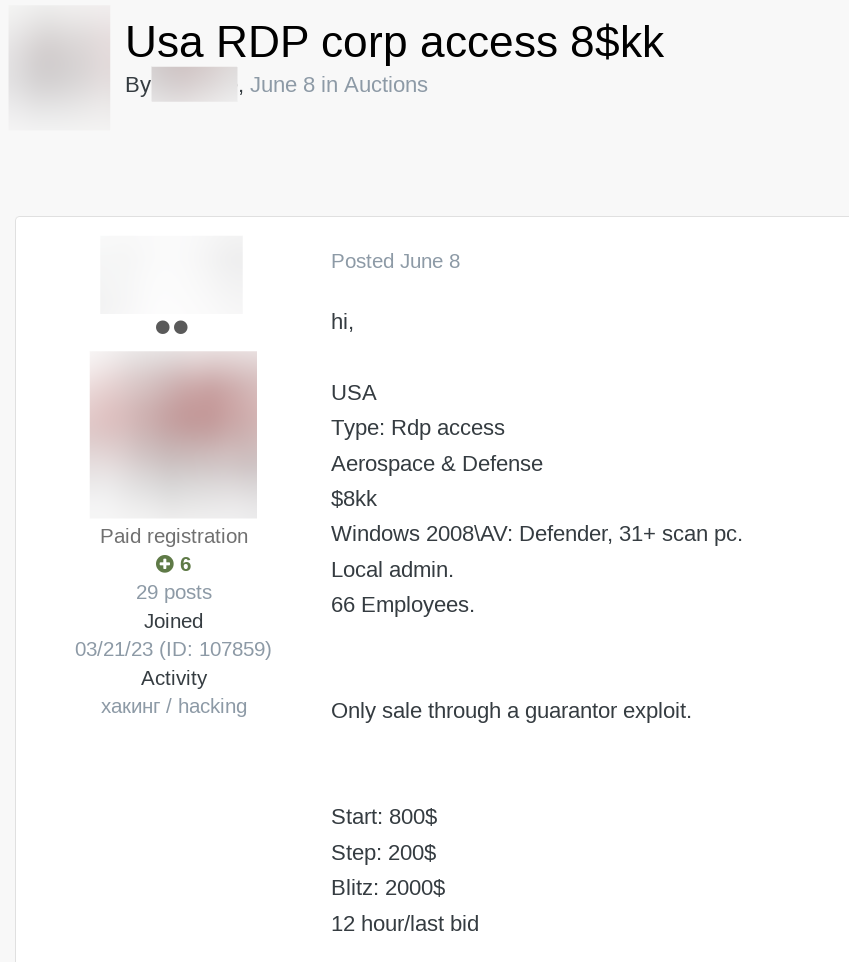
Monitoring Initial Access Brokers on the Dark Web
In some cases there are opportunities to stop attacks in progress. For example, initial access brokers hack into companies then resell the obtained access on specialized dark web forums. Identifying that your organization, or a third-party has network access being sold can be a huge value proposition.
Source: Flare
Another key area of value that organizations can get from dark web monitoring is monitoring
ransomware blogs found on .onion sites. In recent years ransomware groups have increasingly shifted to double and triple extortion schemes, designed to put maximum pressure on the victim to pay the ransom.
As a result, ransomware groups now steal the data prior to encryption, and post it on dark web leak sites if the victim doesn’t pay.
Chances are you would know if you were a victim of ransomware, but many organizations find that a third-party has exposed huge numbers of sensitive files, weeks or months after the fact.
Monitoring ransom leak sites can be of enormous value, particularly if your dark web monitoring platform can parse the file archives and match individual file names.
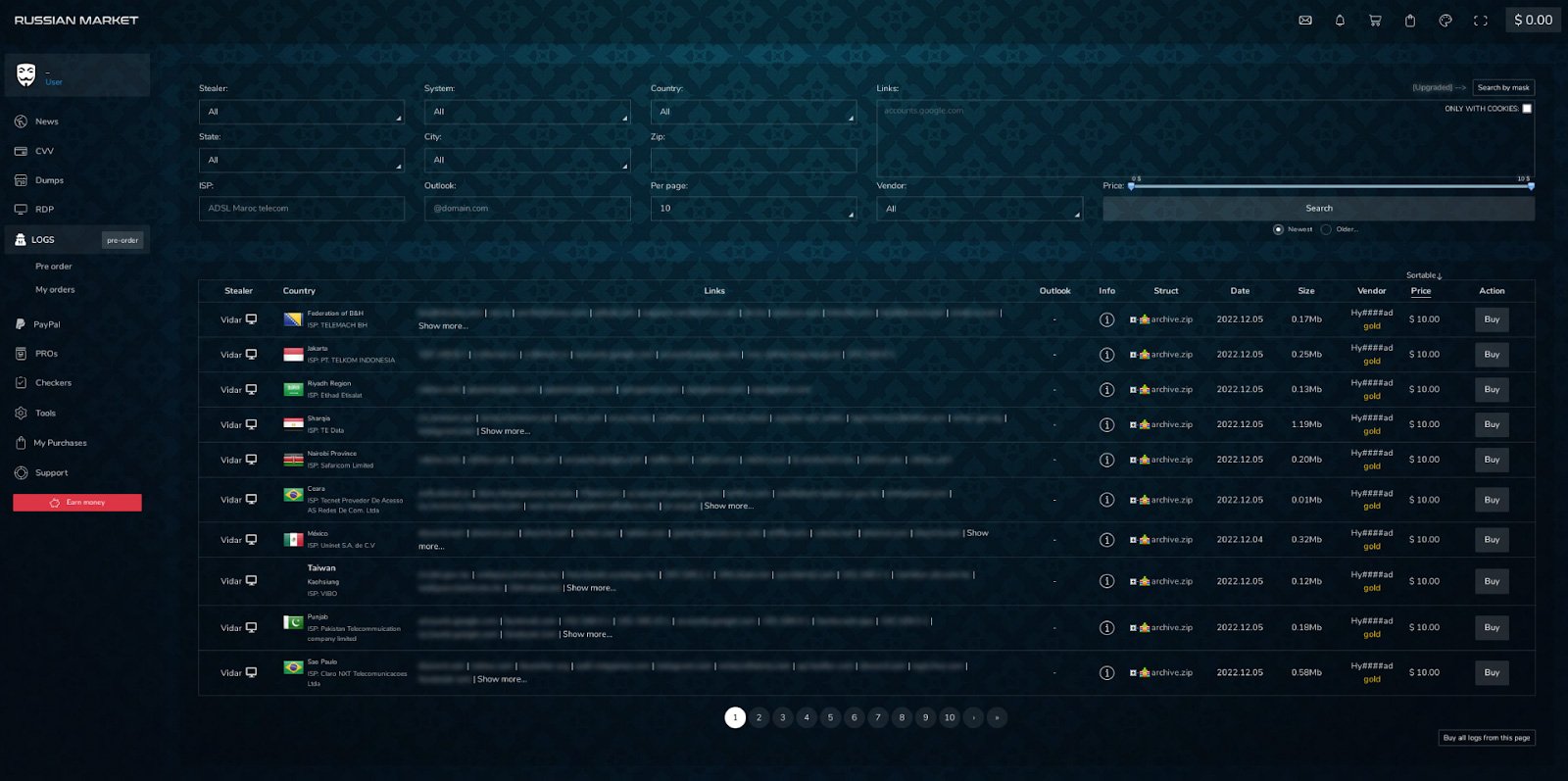
Finally, Russian Market is also a critical source to monitor in 2024. Russian Market is a “stealer logs” marketplace where threat actors sell individual stealer logs.
Source: Flare
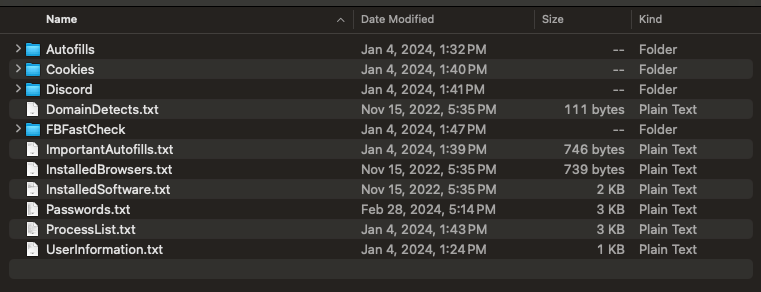
Stealer logs are a result of infostealer malware infections and include all of the saved credentials of a single browser.
For example we recommend monitoring for access to your corporate domain to identify a listing that also contains access to corporate credentials. Stealer logs are a top vector for threat actors and ransomware groups in 2024.
Source: Flare
The Extended Dark Web: Monitoring Telegram, Stealer Logs, and the Evolution of the Cybercrime Ecosystem
The cybercrime ecosystem is no longer confined to .onion sites found on Tor. Threat actors now routinely use instant messaging applications such as Telegram to commit cybercrime, sell data, and interact with each other.
There are now thousands of Telegram channels focused on bank fraud, stolen accounts, credential theft, and stealer log distribution on Telegram.
Flare currently tracks more than 6,000 cybercrime Telegram channels and monitors more than one million stealer logs per week from Telegram for our customers. Telegram, other social media, and P2P instant messaging applications are an absolutely critical vector of growth for the cybercrime ecosystem.
In terms of volume, actionability, and security value, getting comprehensive monitoring of the stealer log ecosystem is absolutely essential. At Flare we estimate that between 5%-10% of stealer logs have corporate credentials, and in some cases have seen CRMs, corporate bank accounts, VPN, and RDP access leaked into Telegram.
Dark web monitoring is not a “low actionability” sales gimmick, it is instead a critical component of an effective information security program that helps organizations identify external threats to their cybersecurity posture.
Dark Web Monitoring with Flare
The Flare Threat Exposure Management (TEM) solution empowers organizations to proactively detect, prioritize, and mitigate the types of exposures commonly exploited by threat actors.
Our platform automatically scans the clear & dark web and illicit Telegram channels 24/7 to discover unknown events, prioritize risks, and deliver actionable intelligence you can use instantly to improve security.
Flare integrates into your security program in 30 minutes and often replaces several SaaS and open source tools.
Learn more by signing up for our free trial.
Sponsored and written by Flare.


Post a Comment Community Rules
You need to login in order to post a comment
Not a member yet? Register Now