
Certain Google-owned domains have caused Chrome users, from even the most skilled researchers to regular users, to question whether they are malicious.
The domains I am referring to are redirector.gvt1.com and gvt1/gvt2 subdomains that have spun many questions on the internet.
After receiving multiple concerned questions over the years, BleepingComputer has dug deeper into the domains' origin and whether they should be something to worry about.
What are these suspicious gvt1.com domains?
The domains *.gvt1.com and *.gvt2.com, along with their subdomains, are owned by Google and typically used to deliver Chrome software updates, extensions, and related content.
For example, when we started Chrome just now, it attempted to connect to the following domains:
http://redirector.gvt1.com/
http://r5---sn-8xgp1vo-ab5z.gvt1.com/
However, these URLs and the domain name has repeatedly caused confusion among developers and researchers due to their suspicious-looking structure:
Likewise, gvt.1com domains have been previously flagged by antivirus products as malware [1, 2] and by researchers as an Indicator of Compromise (IOC) [1, 2, 3].
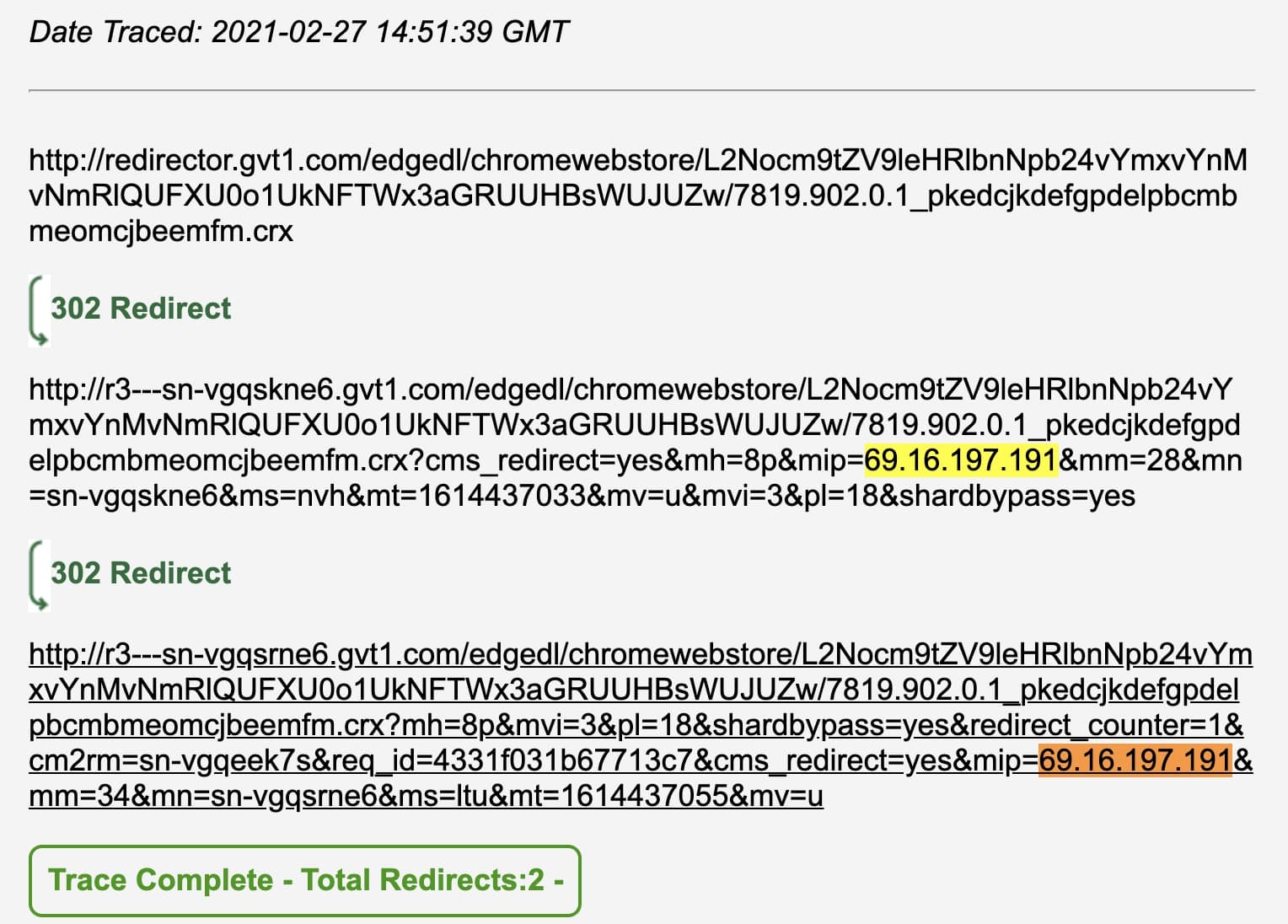
Moreover, the redirector.gvt1.com links redirect to an URL that contains the user's IP address, among other elusive parameters which may cause further suspicion.
For example, BleepingComputer traced the following link, which redirects twice to much larger URLs with an arbitrary subdomain and extensive GET parameters, such as the user's IP address:
http://redirector.gvt1.com/edgedl/chromewebstore/L2Nocm9tZV9leHRlbnNpb24vYmxvYnMvNmRlQUFXU0o1UkNFTWx3aGRUUHBsWUJUZw/7819.902.0.1_pkedcjkdefgpdelpbcmbmeomcjbeemfm.crx
Source: BleepingComputer
Should we be concerned about gvt1.com URLs?
This is where it gets complicated, but the answer is: no, but Google could secure them better.
The GVT in the gvt1.com domain stands for Google Video Transcoding, and is used as a cache server for content and downloads used by Google services and applications.
Put simply, the *.gvt1.com domains are only used by Google to deliver official content, Chrome browser updates, and Android-related executables.
"redirector.gvt1.com is a redirection service used by Google for a variety of purposes, including download of updates, etc.," Eric Lawrence, a former member of the Chrome Security Team, stated in a Google bug post.
Going back to the link analyzed in the previous section as an example, we can see the URL ending in .crx represents a Chrome extension :
http://redirector.gvt1.com/edgedl/chromewebstore/L2Nocm9tZV9leHRlbnNpb24vYmxvYnMvNmRlQUFXU0o1UkNFTWx3aGRUUHBsWUJUZw/7819.902.0.1_pkedcjkdefgpdelpbcmbmeomcjbeemfm.crx
BleepingComputer traced the extension to be the Chrome Media Router extension, a legacy component that was used by Chromecast.
What is concerning, is that Google continues to use the insecure HTTP protocol rather than HTTPS when connecting to these URLs.

By connecting to the URLs via HTTP, it may be possible to use man-in-the-middle (MiTM) attacks to modify the downloads in some manner. If you have malware installed that is intercepting HTTP traffic, you have more to worry about at this point.
In conclusion, when seeing traffic concerning *.gvt1.com or *.gvt2.com domains in your corporate network, it is not a cause for alarm but simply a legitimate Chromium download taking place.
However, Google should switch to using HTTPS to prevent potential MiTM attacks, and administrators should continue to follow best practices such as analyzing traffic from the URLs.
BleepingComputer reached out to Google multiple times well in advance, but we have not heard back before press time.



Comments
Dominique1 - 3 years ago
Nonetheless, we should never tolerate such obfuscation. The path should be clear. For example:
https://pluggin.google.com
That's it!
:facepalm:
U_Swimf - 1 year ago
Oh man... I see this followed by" SQLite leaking fix your app" or some garbage ..along with proxy backend logger . I have auto updates off about every way possible short of changing the buildprop.. so it's not that necessarily... Probably YouTube updating it's next rounds of ads and recommended videos (more ads) with a side of ads (from my leaked sql credentials) fml